Not every individual knows that squamous cell papilloma is the result of a viral disease. In addition to being an aesthetic problem, the disease can seriously harm health, including death. The tumor can "grow" on any part of the body and affect internal organs.
What is squamous cell papilloma and its structure
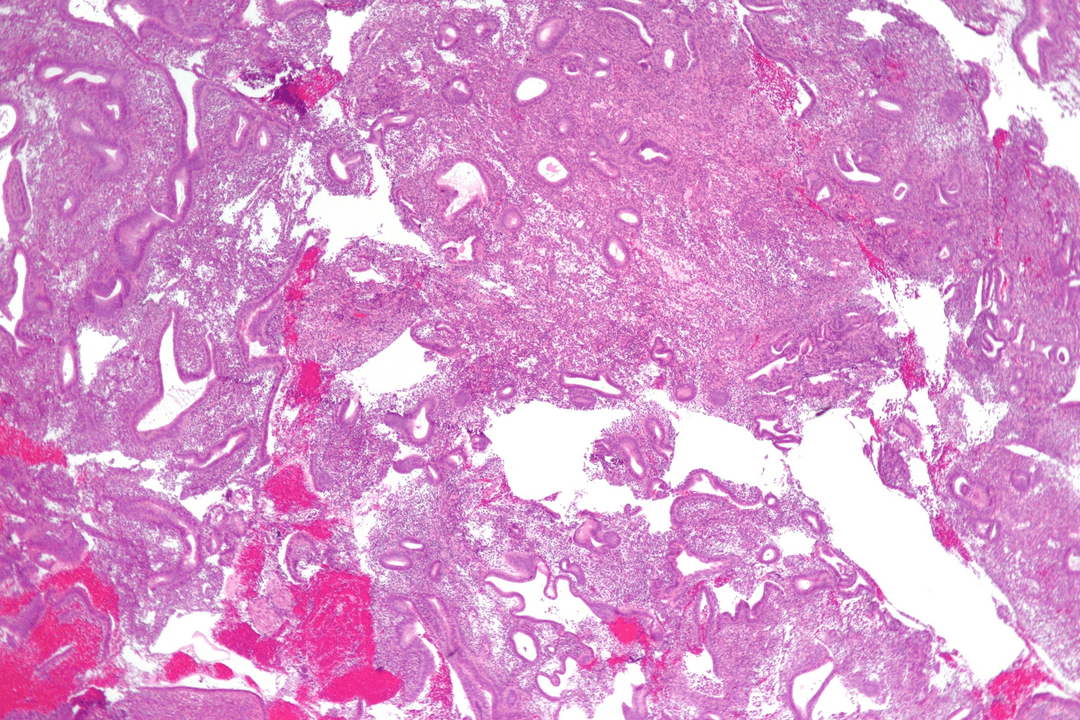
The answer to the question: "What is it? " is a benign neoplasm. The main places of localization include the face, neck, and mucous membranes. If the pathology is not treated for a long time, it can become malignant. Externally, a flat papilloma resembles a mole in the shape of a circle. Color can vary from flesh to deep brown. Doctors call squamous papilloma with hyperkeratosis the most common. It mainly occurs in older people, sometimes in individuals 30-35 years old.
Causes and sources of infection
There are many ways to become infected with squamous cell papilloma of the skin, some of them are simple and do not cause any concern:
- Sexual intercourse of any origin: vaginal, oral, anal;
- Everyday contact (handshake). Fundamental here is the presence of open wounds;
- Visiting public places with high humidity levels: swimming pool, sauna;
- Violation of personal hygiene standards.
This type of papillomas is diagnosed in people with a low level of immunity who have many casual sexual contacts.
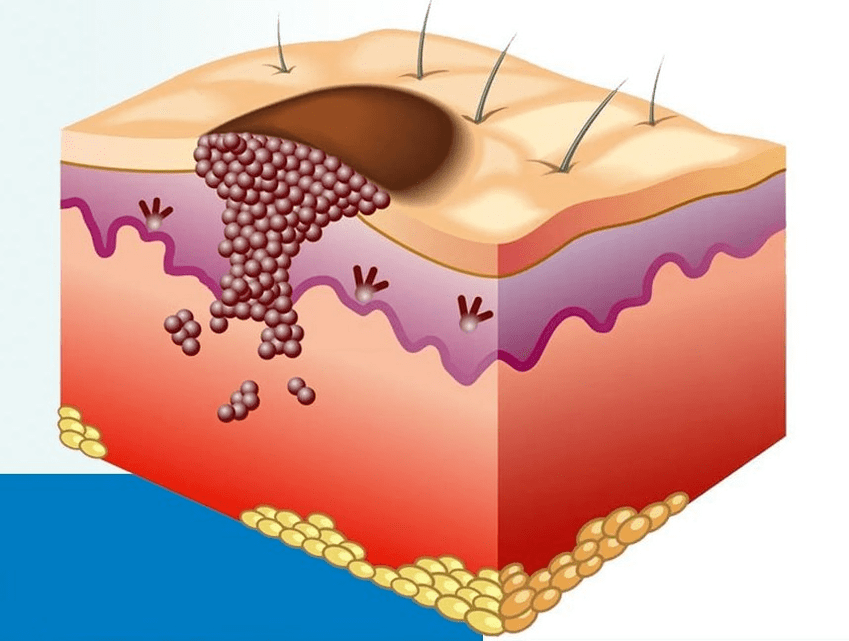
The penetration of a virus into a healthy body does not mean that papillomas will appear in the near future. This only happens when immunity declines. Main reasons:
- Presence of bad habits: alcoholism, smoking, illegal drugs, poor quality nutrition;
- Malfunction of the digestive system;
- Skin diseases;
- Elderly age;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Third-party chemical exposure.
Esophageal papilloma appears almost immediately after a failure. It forms on the tongue, lips, inside the mouth, in the esophagus, and intestines.
Why is it dangerous for humans?
The main danger is that papilloma with hyperkeratosis develops into cancer in more than 60% of cases. If the growth forms in the respiratory system, there is a risk of a gradual lack of oxygen, leading to death. When a growth appears in the intestines, it may fester due to exposure to feces. With squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus, there is a risk of inflammation and bleeding due to eating solid food or low-quality alcohol.
Symptoms and diagnosis
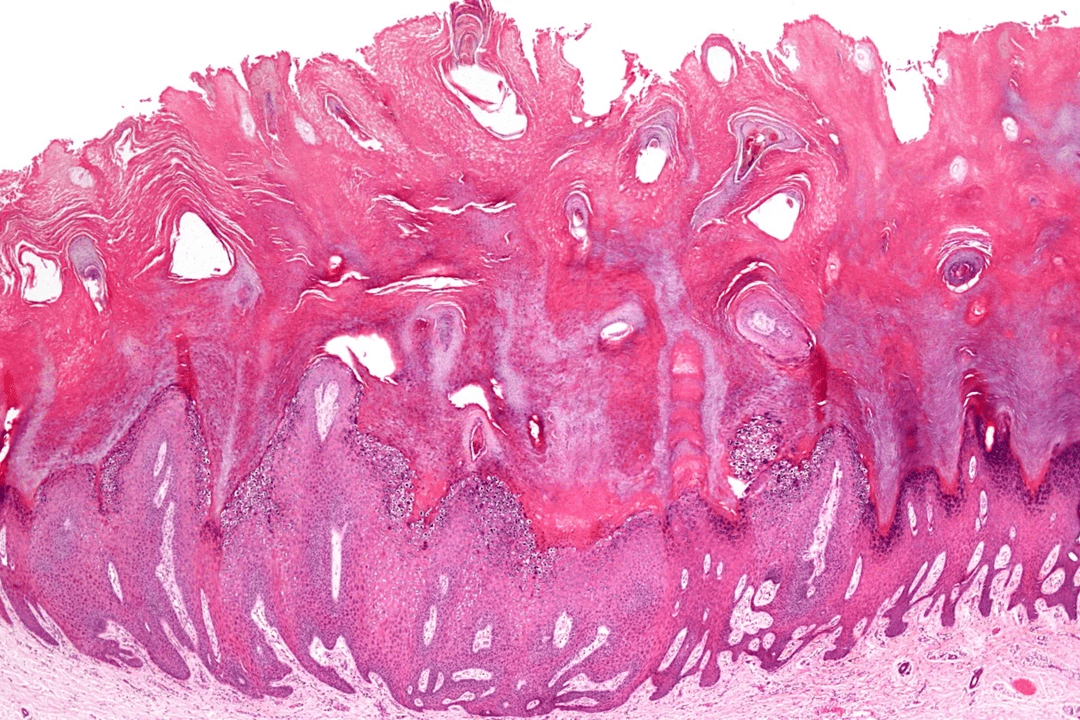
Symptoms of the formation of squamous cell papilloma are few and vague. First, the area with the growth is inspected. Most individuals mistake skin growths for warts and do not pay attention to them, hoping that they will disappear over time. The neoplasm develops and grows very slowly, and inflammation appears very rarely.
Foci of manifestation primarily appear in the thinnest areas of the skin. This is the eyelid area, neck, chest. If the eyelid is affected, damage to the conjunctiva may occur.
The neoplasm grows and develops gradually, its average size is from 0. 3 to 1. 5 centimeters. The color of the neoplasm is different and can change over time from flesh-colored to purple.
Picking, squeezing, or cutting off a squamous cell papilloma is dangerous; an infection can get into an open wound.
There are no special diagnostic measures to detect the presence of the virus. First, a visual examination of the tumor is performed by a therapist. Afterwards, he writes out referrals to other specialists: a dermatologist, a gynecologist. The appointment is made depending on the location of the papilloma. If it is located on the outer part of the skin, the diagnosis can be determined immediately. If the growth is inside the body, fluoroscopy is prescribed.
If the rectum is affected, the doctor palpates the neoplasm; the cervix is clearly visible using a gynecological glass.
There are a number of mandatory procedures:
- Biopsy;
- Blood analysis;
- PCR examination.
If necessary, the treating doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic methods.
Papillomas of the esophagus
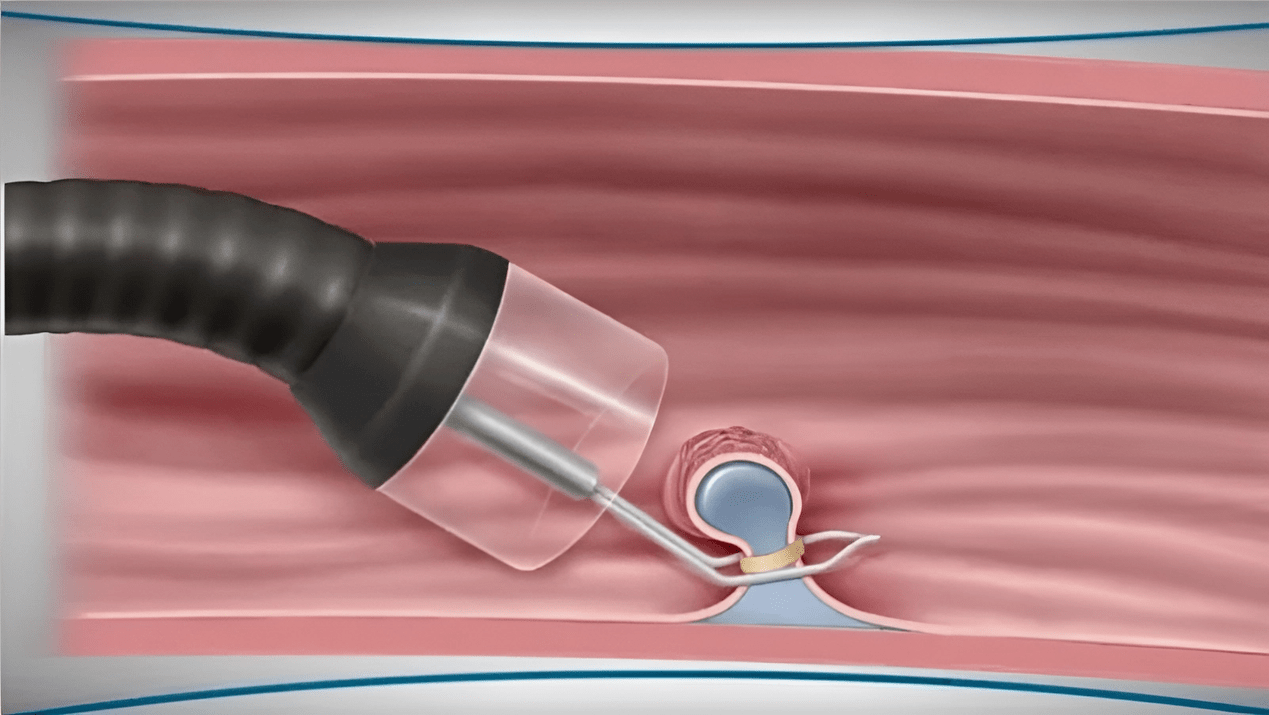
The main sites for the formation of squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus are the tongue, lips, and oral mucosa. The virus may be accompanied by the formation of small ulcers and itching.
With papillomas on the lips, the first thing that appears is swelling and discomfort when eating. If the affected area is damaged, blood appears. The growth can grow quickly and cause lip cancer.
With papilloma of the esophagus, the symptoms of which occur mainly in the male half of the population. The causes of the disease can be poor nutrition, poor quality food, and bad habits. The main location of the tumor in the esophagus is its middle part. The size of each is from 1-2 millimeters to 3-4 centimeters, elongated in shape, on a stalk. The patient notes pain in the stomach, belching, excess salivation, and a lump in the throat. Diagnosis is carried out using radiography and esophagoscopy.
Signs of formations in the mouth and larynx
With squamous cell papilloma of the larynx, it hurts the patient to eat, swallow, and sometimes even breathe. Sometimes there are difficulties with speaking. The size of the growth is small, pedunculated. If a neoplasm is discovered in a child, treatment is not started immediately; it happens that it goes away on its own. If you do not fight the disease in adulthood, it may degenerate into a malignant tumor.
The appearance of squamous cell papilloma of the tongue does not manifest itself in any way at first. White, flesh-colored growths begin to manifest themselves only if the patient has somehow injured them. After a few weeks, bad breath appears, itching, burning, and ulcers form.
Symptoms in the larynx in adults may vary, depending on the general condition of the body and the degree of development of the disease. There may be a sore throat, a lump in the nose, discomfort, congestion, itching. If a growth has formed on the septum, it gradually grows throughout the nasal sinuses, disrupting the normal processes of oxygen entry and exit.
Symptoms of formations in intimate places
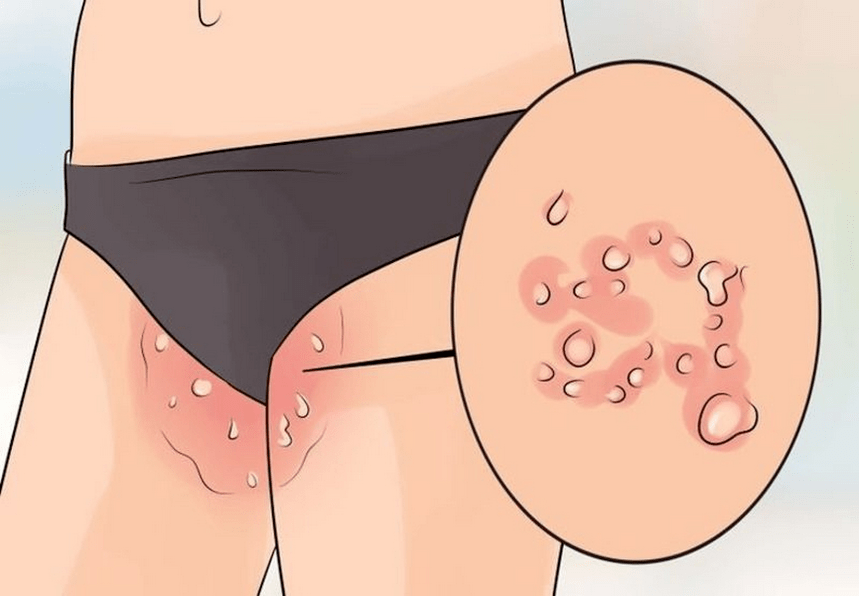
With squamous cell papilloma of the cervix, there is a very high risk of the benign state of the neoplasm turning into cancer. Often this process is accompanied by erosion and genital warts.
At the stage of inception, initial development, the virus does not have any symptoms. Itching and burning gradually appear in the affected area, and over time a constant state of discomfort appears. Discharge is possible. Papilloma is detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist, and colposcopy may be prescribed. During pregnancy, a woman may experience a decrease in her immunity level and, accordingly, the appearance of papillomas. In such cases, immediate removal is recommended.
If we talk about the genitourinary system, the most problematic place for women is the rectum. There are no symptoms at the initial stage, then pain, itching, purulent discharge, and blood in the stool appear. The diagnosis can be made after a palpation procedure. In 90% of cases when this type of neoplasm appears, doctors send you to take tests for syphilis.
Treatment and removal methods
In most cases, patients seek treatment when symptoms are already severe. It is forbidden to prescribe treatment for yourself or try to remove papilloma. Removal is carried out in several ways:
- Cryotherapy using liquid nitrogen;
- Surgery;
- Removal by high frequency current;
- Laser removal;
- Operation using a radio knife.
Esophageal papilloma requires additional examination; accordingly, treatment may take longer.
After the removal procedure, the scar is practically invisible. But there is no 100% guarantee that the tumor will not appear again. Without proper prevention, the virus will wake up again and growths will appear. After treatment, the patient is prescribed a course of antiviral drugs, vitamins, and immunomodulators. It is important to restore the level of general immunity as successfully as possible. Even if the virus remains in the body, it will contain it, preventing the formation of papillomas. It is recommended to eliminate bad habits completely.
Treatment with folk remedies
Squamous cell papilloma, like all other types of growths, forms mainly in elderly people. Surgical intervention is contraindicated for many of them. In such cases, the attending physician advises turning to traditional medicine. The most recommended means are:
- Freshly squeezed potato juice. Course – 2 months, take 100 ml, 2 times a day;
- Celandine juice. Course – 4 weeks, the affected area is lubricated with liquid several times a day;
- Fresh garlic. The cleaned slice is secured to the growth with an adhesive plaster for 2-3 hours.
Currant leaves, licorice root, nettle, lemongrass, plantain, garlic, beets, and carrots are actively used in the preparation of medicinal infusions. In addition to taking medicinal compounds internally, you can prepare salads and soups from medicinal plants and vegetables.
Prevention and prognosis
The main preventive methods are:
- Early seeking of medical help;
- Proper nutrition;
- Elimination of all bad habits.
Papilloma of the esophagus, bladder, and cervix "responds" well to natural traditional medicine. Their treatment is also slightly different from the traditional one; it also takes longer.
After removal surgery, rehabilitation can proceed differently, and complications may occur. Basically, the forecasts are always favorable. The percentage of deaths is minimal. If the process of formation of cancer cells has already begun, the survival rate is 30-35%.
If you seek medical help in time, a complete cure is 90% possible, and soft tissue damage is minimal. Cancerous tumors are also successfully removed, and the process of degeneration can be stopped.













































































